Primary Care Services
Non Surgical Knee Pain Treatment
Non Surgical Knee Pain Treatment Knee pain is one of the most common issues we have seen developing as we age. Knee pain can have various causes, from acute injuries to chronic conditions. What are the Knee pain causes?…
Telehealth Medicine
Telehealth Medicine Telehealth appointments ( both via phone and virtually via video call ) are available for patients with Counselling Needs Discussion of lab results Patients who have tested positive for cOVID screening questions Please note that we are…
Dermatological Procedures Essential to Primary Care
Use of cryofreeze ( liquid nitrogen) to remove sking tags /warts Use of hyfrecator to remove skin tags , skin growths , syringoma
Paps Smear
Paps Smear Pap test, also called a Pap smear, is a routine screening test for early diagnosis of cervical cancer. Dr.Garg has been doing routine paps smear on all her female patients since past 12+ years . What…
Joint Injections
Joint Injections Most primary care physicians find injecting joints, bursae, tendon sheaths, and soft tissues of the human body a useful diagnostic and therapeutic technique. For many common conditions, extensive practice-based experience supports the success of joint and soft…
Preventive Care Annual Physical
Preventive Care Annual Physical visit involves the below: Age-Appropriate Cancer Screenings Age and risk appropriate Vaccinations STD screening as needed Tobacco and Alcohol abuse Counselling as needed Screening Labs as needed Screening for osteoporosis and fall prevention counselling as…
Ongoing Care for Chronic Illness
Evaluation and treatment of chronic medical ailments Regular clinical visits Regular lab monitoring Specialists’ referrals as appropriate Care coordination with different specialists Prompt outpatient follow up after a recent hospitalization or recent sick visit to ER
In House Labs and Testing
In House Labs and Testing We are well equipped to do simple but highly relevant in-house procedures like : Urine dipsticks for Urinalysis Urine Pregnancy Tests Rapid Strep Tests Rapid Flu tests Sugar check Checking and interpreting EKG
In house injectables and treatment
We are well-equipped to do the following injectables and treatments in-house: Nebulizer treatment for acute asthma exacerbation Same face-to-face STD treatment including Expediated Partner therapy in the treatment of Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Intramuscular Ceftriaxone for treatment of PID as…
Primary Care
Primary Care Overview
Primary care is often the first point of care for most patients with an undiagnosed symptom, sign, or health concern. Dr. Garg has been highly trained and doing primary care for more than 15 years. As part of her role as a primary care provider, she provides diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of most chronic medical problems such as diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and asthma. Also, she conducts regular and comprehensive physical exams every year.
In addition, she responsibly coordinates care with other health services related to a patient’s care as necessary. She is also board certified in Primary care, Psychiatry and can help manage common psychiatric ailments presented in primary care settings.
What are the different primary care types of visits?
Primary care visits encompass a range of services provided by healthcare professionals who serve as the first point of contact for individuals seeking healthcare. Here are some common types of primary care visits:
- Establish care visits: Establishing care involves developing a lasting relationship with a primary care provider (PCP) who will serve as your main contact for all your routine medical needs.
- Preventive Care Visits: These visits focus on maintaining good health and preventing illness. They often include vaccinations, screenings, and advice on healthy lifestyle choices. These are routine visits to monitor and assess a person’s overall health. They may involve checking vital signs, reviewing medical history, and discussing concerns.
- Sick Visits: These appointments occur when experiencing acute health problems or symptoms. They can address issues like infections, minor injuries, or sudden illnesses.
- Chronic Disease Management: Individuals with long-term or chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, asthma, or arthritis may have regular appointments to manage and monitor their condition.
- Lab Follow-up Visits: These appointments are scheduled after a previous visit to assess progress, discuss test results, or adjust a treatment plan.
- Medication Management: Some primary care visits are dedicated to reviewing and managing medications, including prescription renewals and adjustments.
- Women’s Health Visits: These appointments may include gynecological exams, Pap smears, breast exams, and discussions about contraception or family planning.
- Men’s Health Visits: These appointments focus on health issues specific to males, including prostate exams, testosterone level checks, and discussions about sexual health.
- Sports Physicals for Adults: These are specialized exams for athletes to ensure they are fit and healthy for sports activities.
- Travel Health Consultations: These appointments provide advice and vaccinations for individuals planning to travel abroad to areas with specific health risks.
Remember that the specific types of primary care visits may vary depending on your country’s healthcare provider and healthcare system. It’s always a good idea to communicate with your primary care provider to understand their services and schedule the appropriate visit based on your health needs.
What is done in an establish-care visit as part of primary care?
An established care visit, or an initial or comprehensive visit, is the first appointment with a new primary care provider (PCP) or healthcare facility. Its purpose is to establish a baseline of your health and medical history and build a relationship with your healthcare provider. Here’s what typically happens during an established care visit:
- Medical History Review: You’ll be asked about your medical history, including any previous illnesses, surgeries, chronic conditions, allergies, and medications you’re currently taking.
- Family History Discussion: Your provider may inquire about the health of your immediate family members (parents, siblings) and extended family to identify potential genetic predispositions or hereditary conditions.
- Personal Health Habits and Lifestyle Assessment: Your healthcare provider might ask about your diet, exercise routine, smoking or alcohol habits, and any recreational drug use. This information helps in understanding your overall health and well-being.
- Vital Signs Check: This includes measurements like blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and sometimes body temperature. These numbers provide important indicators of your current health status.
- Discussion of Health Concerns: You’ll have the opportunity to discuss any current health issues, symptoms, or concerns you may have. This could range from minor discomforts to more serious symptoms.
- Immunization Review: Your provider will ask about your vaccination history to ensure you are up-to-date on recommended vaccines.
- Screening Tests and Labs: Depending on your age, gender, and health history, your provider may recommend specific screenings like cholesterol checks, blood sugar tests, or cancer screenings.
- Referrals and Specialist Recommendations: If necessary, your primary care provider may refer you to specialists or recommend additional tests or consultations.
- Establishing a Follow-up Schedule: Your provider will discuss when to return for routine check-ups or follow-up visits based on your health needs.
- Building a Patient-Provider Relationship: This visit establishes a rapport between you and your healthcare provider. Clear communication and trust are essential for effective healthcare.
Remember that every healthcare provider may have a specific approach to an established care visit, so the exact sequence and details may vary. During this visit, it’s important to be open and honest to ensure your provider comprehensively understands your health.
Establishing care entails starting a long-term relationship with a single primary care provider (PCP), who will serve as your go-to resource for all of your regular medical requirements. Your PCP may help ensure your health for a very long time by advising you on how to maintain it, treating various ailments and wounds, and assisting you in getting specialty care when you require it. Your initial appointment with your PCP will be billed as “establishing care.”
Once you establish with our clinic, you can reach out to the doctor anytime during the week, and she responds to patient messages within 24 hours. We also provide short-notice sick visits for any established patients.
What is done in an annual physical / preventive primary care visit?
The annual physical primary care visits are extremely important to diagnose any problems and do age, gender, and family history-specific screens. The annual physical visits can differ for patients if they fall into one of the below categories. Hence, it is difficult to do an annual physical on the first visit as the doctor needs to know your and family’s medical history before she can do the physical.
- Pregnant persons
- Patients with HIV
- Cancer survivors
- Patients with diabetes mellitus
- Older adults
- Transgender men and women
Priority health issues and successful interventions should be the focus of preventive care. We individualize screening and prevention measures to optimize value, which includes the tradeoffs between benefits, risks, and costs, as opposed to doing a standard comprehensive examination (or “full physical”) on every patient. Any precise rules do not constrain the recommended frequency of periodic visits, and there is no supporting data to base this suggestion.
You don’t need to visit the doctor yearly if you’re young and healthy. But if you have a chronic condition like diabetes, heart disease, cancer, or other long-term illnesses, you should get frequent checkups to stay healthy. For people over 49 who don’t have any chronic issues, it’s recommended to get a checkup every three years. Once you turn 50, it’s best to get a yearly checkup. These checkups can help prevent health problems and allow you to talk with your doctor about staying healthy.
During an annual physical or preventive primary care visit, a doctor aims to assess your overall health, identify potential risk factors or early signs of disease, and provide guidance for maintaining or improving your well-being. Here’s what typically happens during such a visit:
- Review of Medical History: The doctor will review your medical history, including any existing conditions, past surgeries, allergies, medications, and family medical history. This provides important context for your current health.
- Discussion of Lifestyle and Habits: They’ll ask about your lifestyle choices, including your diet, exercise routine, smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use. This information helps in understanding your overall health and well-being.
- Vital Signs Assessment: This includes measuring your blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and sometimes body temperature. These measurements provide important indicators of your current health status.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will perform a thorough physical exam. This may include checking your head, eyes, ears, nose, throat (HEENT exam), chest, abdomen, extremities, skin, and neurological functions.
- Immunization Review: The doctor will ask about your vaccination history to ensure you are up-to-date on recommended vaccines. They may recommend any necessary vaccinations based on your age and health status.
- Discussion of Health Concerns: You’ll have the opportunity to discuss any current health issues, symptoms, or concerns you may have. This could range from minor discomforts to more serious symptoms.
- Nutrition and Exercise Guidance: The doctor may advise on maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity to promote overall health and prevent chronic conditions.
- Mental Health Assessment: They may ask about your mental health, including any symptoms of anxiety, depression, or stress. They can offer guidance or referrals to mental health professionals if needed.
- Preventive Measures and Health Promotion: The doctor will discuss the importance of preventive measures such as vaccinations, screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices.
- Review of Medications: If you take any medications, the doctor will review them and make adjustments or provide recommendations as needed.
- Referrals and Specialist Recommendations: If necessary, the doctor may refer you to specialists or recommend additional tests or consultations.
Remember that the specific details of an annual physical or preventive primary care visit may vary based on your age, gender, and individual health needs, as well as the preferences and practices of your healthcare provider. Communicating openly and honestly with your doctor during this visit is important.
What is ongoing care for chronic illness / Chronic Disease Management in primary care?
It is extremely important to keep chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, cancer, chronic lung, stroke, Alzheimer’s, chronic kidney disease, etc., under control; hence we need to check the key parameters/labs periodically and adjust medication based on that.
As an example, the tables below describe the monitoring of Diabetes Mellitus as per the Uptodate article.
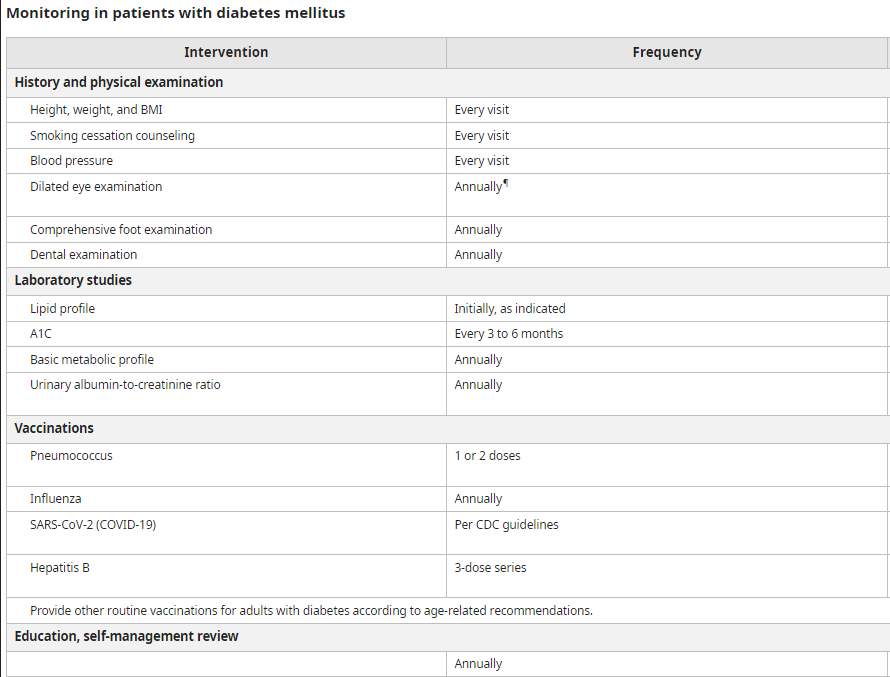 Based on the patient’s lab results, the doctor provides counseling and adjusts medication to get the diabetes under control. Often, patients might need to be counseled to reduce weight and asked to enroll in a weight loss program like Meal Replacement. We do have an effective weight loss program. We have seen our patients struggling with diabetes, and after they enroll in our program, they can lead a more active lifestyle, and their diabetes gets into control with normal A1C levels. They lose 20-25 pounds within two months or so.
Based on the patient’s lab results, the doctor provides counseling and adjusts medication to get the diabetes under control. Often, patients might need to be counseled to reduce weight and asked to enroll in a weight loss program like Meal Replacement. We do have an effective weight loss program. We have seen our patients struggling with diabetes, and after they enroll in our program, they can lead a more active lifestyle, and their diabetes gets into control with normal A1C levels. They lose 20-25 pounds within two months or so.
What is done in acute issues or sick visits during primary care?
People can sometimes get known or unknown issues like allergic reactions or asthma attacks. Again, we advise you to go to the Emergency Room if it is a life-threatening condition. If you have a sickness that is not life-threatening, then you can consider calling us and booking a same-day virtual visit with our doctor. We try to give preference to our established patients for sick visits where a doctor can also respond to your messages and give her feedback on your condition.
If needed, the doctor will order labs and refer you to a specialist to get an expert opinion and treatment. We know that specialist visits can be expensive, so we keep this in mind when referring the patient and try to do our best to address concerns as much as possible.
What is done in a lab follow-up visit in primary care?
A lab follow-up visit with a doctor typically occurs after undergoing specific laboratory tests or diagnostic procedures. These visits are focused on discussing the results of these tests and their implications for your health. Here’s what typically happens during a lab follow-up:
- Review of Test Results: The doctor will go over the results of the laboratory tests or diagnostic procedures you’ve undergone. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, biopsies, or other specialized tests.
- Explanation of Findings: The doctor will explain the significance of the test results and what they indicate about your health. They will clarify any medical terminology and ensure you understand the implications.
- Assessment of Health Status: Based on the test results, the doctor will assess your current health status and discuss any potential health concerns or conditions that have been identified.
- Discussion of Treatment Options: If the test results reveal a new diagnosis or a change in your existing condition, the doctor will discuss treatment options, which may include medications, lifestyle changes, or other interventions.
- Medication Review: If treatment involves medications, the doctor may review any prescribed drugs, their dosages, potential side effects, and instructions on how to take them.
- Recommendations for Further Testing: Depending on the results, the doctor may recommend additional tests or follow-up procedures to gather more information or monitor a specific aspect of your health.
- Development of a Care Plan: Together with your doctor, you’ll develop a care plan that outlines the next steps, treatment goals, and a schedule for follow-up visits or additional testing.
- Discussion of Lifestyle Modifications: If applicable, the doctor may guide lifestyle modifications that can support your health, such as dietary changes, exercise routines, or stress management strategies.
- Addressing Questions and Concerns: You’ll have the opportunity to ask questions and express any concerns or uncertainties you may have regarding your test results and recommended treatment plan.
- Mental and Emotional Support: If the test results or diagnosis have emotional or psychological implications, the doctor may discuss these aspects and offer resources or referrals to mental health professionals if needed.
- Follow-up Schedule: The doctor will establish a schedule for follow-up visits to monitor your progress and the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
- Building Trust and Rapport: Lab follow-up visits are important for maintaining a strong patient-provider relationship, as they involve in-depth discussions about your health and treatment.
Lab follow-up visits are critical for ensuring you receive appropriate care based on the information gathered from diagnostic tests. It’s important to actively participate in these appointments, ask questions, and seek clarification to understand your health status and treatment plan fully.
What is expected in a medication management visit during primary care?
A Medication Management visit with a doctor specifically focuses on reviewing and optimizing your medications. The aim is to ensure that you are taking the right medications at the correct doses and that they are effectively managing your health condition. Here’s what typically happens during a Medication Management visit:
- Review of Current Medications: The doctor will review all the medications you are currently taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, supplements, and vitamins.
- Assessment of Medication Effectiveness: The doctor will discuss how well your current medications manage your health condition. They will inquire about any improvements or changes in your symptoms.
- Evaluation of Side Effects: You’ll discuss any potential side effects or adverse reactions you may be experiencing from your medications. This includes physical symptoms as well as any impact on your daily life.
- Medication Adherence: The doctor will ask about your adherence to the prescribed medication regimen. Open communication about any difficulties or concerns with taking your medications is important.
- Potential Interactions: The doctor will review whether there are any potential interactions between your medications, and if any adjustments need to be made to avoid adverse effects.
- Dosage Adjustments: Based on your health status and how you’re responding to your current medications, the doctor may recommend changes to dosages or even consider switching to a different medication.
- New Medication Recommendations: If necessary, the doctor may prescribe new medications or suggest additions to your current regimen to manage your health condition better.
- Education and Instructions: The doctor will provide detailed instructions on taking your medications, including dosages, timing, and special considerations (e.g., with or without food).
- Monitoring Plan: They’ll discuss a plan for monitoring your health while on the prescribed medications, including any necessary follow-up visits or tests.
- Addressing Concerns or Questions: You’ll have the opportunity to ask any questions or express concerns about your medications, including potential side effects, interactions, or any lifestyle adjustments needed.
- Discussing Alternative Treatments: In some cases, the doctor may discuss alternative treatment options, including non-pharmacological or complementary therapies.
- Providing Written Information: The doctor may provide written information about your medications, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and any precautions to be aware of.
- Reviewing Special Considerations: If applicable, the doctor will discuss any special considerations related to your medications, such as pregnancy, breastfeeding, or specific health conditions.
- Follow-up Schedule: The doctor will establish a schedule for follow-up visits to monitor your progress and the effectiveness of the medication adjustments.
Remember, medication management visits are a collaborative effort between you and your doctor. Open communication about how you’re feeling and any concerns you may have about your medications is essential for ensuring that your treatment plan is tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
What is performed by doctors during women’s health visits in primary care?
During a Women’s Health visit, a healthcare provider, often an obstetrician-gynecologist (OB-GYN) or a primary care physician with training in women’s health, addresses a range of health concerns specific to women. Here’s what typically happens during a Women’s Health visit:
- Medical History Review: The doctor will review your medical history, including any gynecological or reproductive health concerns, pregnancies, menstrual history, contraception methods, and any relevant family history.
- Physical Examination: This may include a pelvic exam, breast exam, and possibly a Pap smear or other specialized exams based on your age and specific health concerns.
- Discussion of Menstrual Health: The doctor may ask about your menstrual cycle, including its regularity, flow, and associated pain or discomfort.
- Pregnancy and Fertility: If applicable, the doctor may discuss pregnancy planning prenatal care, and provide information about fertility.
- Contraception and Family Planning: The doctor will discuss contraception options, including birth control pills, intrauterine devices (IUDs), condoms, and other methods. They’ll help you choose a method that aligns with your reproductive goals and lifestyle.
- Screening for Gynecological Conditions: This may include screenings for conditions like cervical cancer (Pap smear), breast cancer, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and other gynecological concerns.
- Breast Health and Education: The doctor will perform a breast exam and may provide information on breast self-exams and the importance of mammograms for breast health.
- Sexual Health and Intimacy: The doctor may ask about your sexual health, including any concerns or issues related to sexual activity, libido, or pain during intercourse.
- Menopause and Hormone Replacement Therapy: For women approaching or experiencing menopause, the doctor may discuss symptoms, management strategies, and the potential benefits and risks of hormone replacement therapy.
- Bone Health: The doctor may provide information on maintaining bone health, especially for postmenopausal women, to prevent osteoporosis.
- Urinary Health: If relevant, the doctor may address concerns about urinary incontinence or urinary tract infections.
- Pelvic Health: The doctor may discuss pelvic floor health, including exercises and strategies for maintaining pelvic health.
- Counseling and Education: They may offer counseling and education on various topics, including sexual health, reproductive choices, and general well-being.
- Vaccinations and Preventive Care: The doctor may discuss and provide HPV vaccine, flu shot, and other immunizations important for women’s health.
- Referrals and Specialist Recommendations: If needed, the doctor may refer you to specialists for further evaluation or treatment of specific women’s health issues.
Remember that the specifics of a Women’s Health visit may vary based on your age, reproductive status, and individual health needs. Communicating openly with your healthcare provider about any concerns or questions about your reproductive and gynecological health is important.
What is performed during the Men’s Health Visits in primary care?
During a Men’s Health visit, a healthcare provider, often a primary care physician or a urologist, addresses health concerns specific to men. Here’s what typically happens during a Men’s Health visit:
- Medical History Review: The doctor will review your medical history, including any previous illnesses, surgeries, chronic conditions, and family medical history.
- Physical Examination: This includes a thorough physical exam to assess general health, including checking vital signs, heart and lung function, and examining various body systems.
- Prostate Health: For men over a certain age (usually 50 and older), the doctor may discuss prostate health, including the risks and benefits of prostate cancer screening tests like the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test.
- Testicular Health: The doctor may perform a testicular exam to check for abnormalities, lumps, or signs of testicular cancer.
- Cardiovascular Health: The doctor may assess cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and discuss lifestyle modifications to support heart health.
- Sexual Health and Function: They may inquire about sexual health, including erectile function, libido, and any concerns related to sexual performance or satisfaction.
- Reproductive Health and Fertility: If relevant, the doctor may discuss fertility and family planning issues.
- Prostate and Colorectal Cancer Screening: Depending on age and risk factors, the doctor may discuss the importance of colorectal cancer screening.
- Urinary Health: They may inquire about urinary function and address concerns about urinary tract health or issues like urinary incontinence.
- Bone Health: The doctor may provide information on maintaining bone health, which is especially important for older men to prevent osteoporosis.
- Lifestyle and Behavioral Health: They may discuss lifestyle habits such as diet, exercise, smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress management.
- Mental Health and Emotional Well-being: The doctor may inquire about mental health, including symptoms of anxiety, depression, or stress. They can offer guidance or referrals to mental health professionals if needed.
- Vaccinations and Preventive Care: The doctor may discuss and provide vaccinations or screenings important for men’s health, such as vaccinations for influenza, tetanus, or HPV.
- Referrals and Specialist Recommendations: If necessary, the doctor may refer you to specialists for further evaluation or treatment of specific men’s health issues.
- Health Education and Counseling: The doctor may offer counseling and education on various topics, including sexual health, reproductive choices, and general well-being.
Remember that the specifics of a Men’s Health visit may vary based on your age, individual health needs, and any specific concerns you may have. Open communication with your healthcare provider about any questions or concerns related to your health is crucial for receiving personalized care.
What is performed during Sports Physicals for adults in primary care?
A sports physical, a pre-participation physical examination (PPE), is a comprehensive medical evaluation designed to assess an individual’s fitness and readiness to participate in sports or physical activities. Here’s what typically happens during a sports physical for adults:
- Medical History Review: The healthcare provider will review your medical history, including any previous injuries, surgeries, chronic conditions, allergies, and medications.
- Discussion of Symptoms and Concerns: They will ask about any current or past exercise-related symptoms, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, or joint pain.
- Vital Signs Check: This includes measurements like blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and sometimes body temperature. These numbers provide important indicators of your current health status.
- Physical Examination: The provider will perform a thorough physical exam, which may include checking your head, eyes, ears, nose, throat (HEENT exam), chest, abdomen, extremities, skin, and neurological functions.
- Vision and Hearing Screening: This may involve a basic assessment of vision and hearing to ensure they meet the requirements for sports participation.
- Musculoskeletal Assessment: The provider will evaluate your strength, flexibility, and joint mobility, particularly in areas prone to sports-related injuries.
- Neurological Assessment: This may include coordination, reflexes, and sensory function tests to ensure no underlying neurological issues could impact participation.
- Cardiovascular Examination: The doctor may listen to your heart and lungs to check for any abnormalities or signs of cardiovascular issues that could affect your ability to engage in physical activity.
- Exercise History and Habits: The provider may ask about your current exercise routine, training habits, and previous involvement in organized sports.
- Assessment of Overall Fitness: The provider will evaluate your physical fitness level, considering factors like endurance, strength, and agility.
- Discussion of Exercise Goals: The provider may offer guidance or recommendations if you have specific goals or aspirations related to your athletic performance.
- Nutritional Guidance: The provider may offer advice on maintaining a balanced diet to support your athletic endeavors.
- Injury Prevention Strategies: They may provide recommendations for injury prevention, such as warm-up exercises, proper technique, and the use of protective equipment.
- Discussion of Any Required Clearances: If you have a specific medical condition or have undergone recent medical treatment, the provider may discuss whether you require additional clearance to participate in certain activities.
- Recommendations for Follow-up or Specialist Evaluation: If any concerns or potential issues are identified during the sports physical, the provider may recommend follow-up visits or refer you to specialists for further evaluation or treatment.
Remember that the specific details of a sports physical may vary based on individual health history, the type of sports or activities you’re participating in, and the preferences of the healthcare provider conducting the examination. The goal is to ensure you can safely and effectively engage in physical activity without compromising your health.
What can I expect in a travel consultation visit as part of primary care?
A Travel Health Consultation is a specialized appointment with a healthcare provider to discuss health considerations and receive recommendations before embarking on international travel. Here’s what typically happens during a Travel Health Consultation:
- Review of Travel Itinerary: The healthcare provider will ask about the specific destinations you plan to visit and the duration and purpose of your trip. This information helps determine which health risks may be relevant.
- Medical History Review: The doctor will go over your medical history, including any pre-existing conditions, allergies, vaccinations, and medications you’re currently taking.
- Discussion of Health Risks: The provider will provide information about potential health risks in the regions you visit. This may include infectious diseases, environmental hazards, and other health concerns.
- Vaccination Review and Recommendations: Based on your travel itinerary and existing immunizations, the doctor will recommend any additional vaccinations or booster shots needed for specific destinations. This may include vaccinations for hepatitis, typhoid, yellow fever, and more.
- Prescription Medications: If you require prescription medications (e.g., malaria prophylaxis, antibiotics for traveler’s diarrhea), the doctor will provide appropriate prescriptions and instructions.
- Prevention of Mosquito-Borne Illnesses: The provider will offer advice on protecting yourself against diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus.
- Food and Water Safety: They’ll guide safe food and water practices to avoid foodborne illnesses.
- Altitude Sickness Prevention: If you are traveling to high-altitude destinations, the doctor may discuss strategies for acclimatization and provide recommendations for managing altitude sickness.
- Personal Health Measures: The provider will advise on general health practices, such as hand hygiene, sun protection, and safe sexual practices.
- Traveler’s First Aid Kit: They may recommend specific items to include in a traveler’s first aid kit, such as over-the-counter medications, bandages, and other essentials.
- Health Insurance and Medical Facilities: The doctor may discuss the availability of healthcare services in the regions you’ll be visiting and recommend travel insurance or medical evacuation coverage.
- Advice for Special Populations: If you have specific health concerns or conditions (e.g., pregnancy, immunocompromised status), the provider will offer tailored recommendations.
- Cultural Considerations: The doctor may advise on cultural sensitivities or health practices specific to the regions you visit.
- Documentation and Records: They’ll make sure you have all necessary documentation, including vaccination certificates, prescriptions, and any relevant medical records.
- Post-Travel Health Considerations: The provider may discuss any potential health risks or symptoms to be aware of after returning from your trip.
It’s important to schedule a Travel Health Consultation well before your trip, as some vaccinations may require multiple doses over some time. Additionally, some destinations may have specific entry requirements regarding vaccinations and health certificates.
Why do you prefer annual physical post-establishing care for a new patient?
Performing an annual physical after establishing care for a patient allows for a more comprehensive and personalized assessment of their health. Here are some reasons why it often makes more sense to do so:
- Established Patient-Provider Relationship: By waiting until after the patient has established a relationship with their healthcare provider, there is a foundation of trust and familiarity. This can lead to more open and honest communication, which is crucial for effective healthcare.
- Comprehensive Medical History: An established patient would have already provided a detailed medical history, including information about existing conditions, past surgeries, allergies, medications, and family medical history. This information is essential for understanding the patient’s overall health.
- Continuity of Care: With an established relationship, the healthcare provider has a better understanding of the patient’s health needs, preferences, and any ongoing issues. This allows for a more personalized and targeted approach to the annual physical.
- Better Context for Physical Exam Findings: Prior knowledge of the patient’s baseline health status allows the provider to interpret the findings of the physical examination better. They can identify new or changing issues and monitor existing conditions more effectively.
- Individualized Screening and Recommendations: With knowledge of the patient’s health history, the provider can tailor the annual physical to focus on specific screenings and assessments most relevant to the patient’s age, gender, and health status.
- Optimal Timing for Preventive Care: Waiting until after establishing care allows the provider to schedule the annual physical at an optimal time for the patient’s health needs. This may involve coordinating with other screenings or assessments.
- Preventive Care Planning: With an established patient, the provider can engage in more in-depth discussions about preventive care measures, lifestyle modifications, and strategies for maintaining or improving health.
- Efficient Use of Time: Performing an annual physical on a patient who has already established care can be more efficient. The provider can focus on addressing any new or evolving health concerns and ensuring that all recommended screenings and assessments are completed.
- Long-term Health Planning: An annual physical post-establishing care allows the provider to discuss the patient’s long-term health goals, which can inform treatment plans and lifestyle recommendations.
Overall, waiting until after establishing care for a patient before conducting an annual physical allows for a more personalized and effective approach to their healthcare. It enables the provider to address specific health concerns and tailor preventive care measures to the individual’s needs and circumstances.
What insurance do you accept for primary care visits?
We accept most commercial insurance along with Medicare for medical primary care visits. You can look at the list of insurance on this page.
Do you provide self-pay visits for patients without insurance or visiting kids from abroad?
Yes, we provide sick visits and physicals at attractive self-pay rates. You can check the self-pay pricing on this page.
What are the self-pay rates for vaccines?
We offer vaccines, and labs are self-pay rates in case the patient does not have insurance. You can book an appointment and check the prices on this page.
Where can I look at the travel clinic service you offer?
We offer comprehensive travel exams and vaccines. You can go over the services on this page.
Who We Are
What We Do
Our vision at One Stop is to provide a single getaway for primary care , aesthetic care travel and weight loss medicine. We also prescribe weight medications for eligible candidates. We accept all major insurances.

